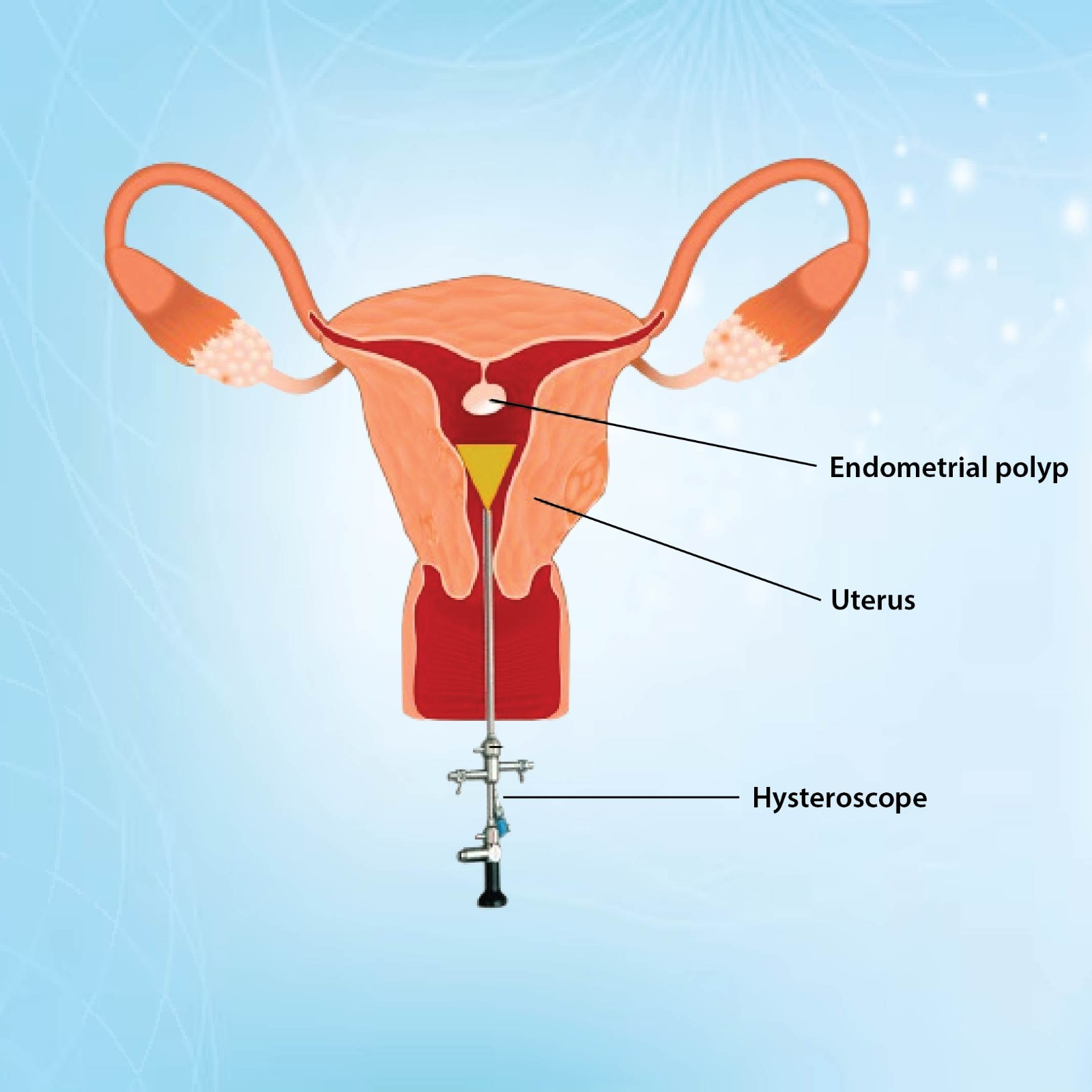
A Hysteroscopy is a valuable minimally invasive procedure that provides a comprehensive view of the inside of the uterus and cervix, utilizing a thin, lighted tube known as a hysteroscope. This diagnostic and therapeutic tool is instrumental in addressing a range of gynecological issues, making it a critical component in women’s health care. By allowing direct visualization, hysteroscopy can help clinicians diagnose conditions such as abnormal uterine bleeding, which may stem from various underlying causes, including hormonal imbalances or structural abnormalities.
Moreover, hysteroscopy plays a significant role in the investigation of infertility and repeated miscarriages. By examining the uterine environment, healthcare providers can identify potential barriers to conception, such as fibroids, polyps, or scar tissue, that could hinder a woman’s ability to achieve or maintain pregnancy. The discovery of noncancerous growths, such as uterine fibroids or polyps, often leads to immediate intervention, allowing for effective removal during the same procedure.