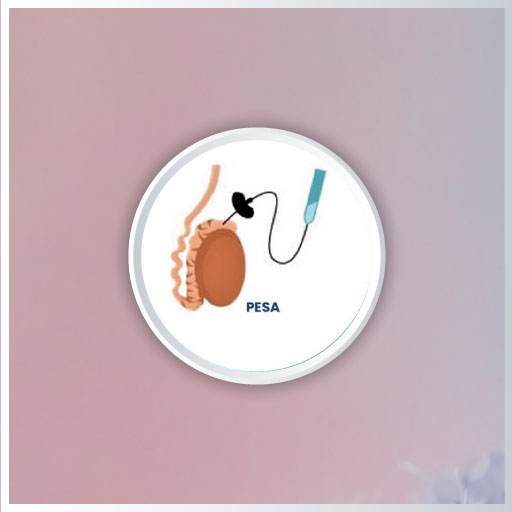
PESA, or Percutaneous Epididymal Sperm Aspiration, is a minimally invasive procedure designed to retrieve sperm from men who are experiencing obstructive azoospermia, a condition characterized by the absence of sperm in the ejaculate due to blockages in the reproductive tract. This blockage can occur as a result of various factors, including prior vasectomy, congenital abnormalities, or infections. In cases where couples seek assistance with infertility and wish to pursue in vitro fertilization (IVF) or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), PESA serves as a critical step in the sperm retrieval process.
During the PESA procedure, a thin needle is inserted into the epididymis—the coiled tube that stores and matures sperm—under local anesthesia. The physician then aspirates fluid containing sperm cells, which are subsequently examined and processed for use in ART procedures. The advantages of PESA include its ability to provide sperm without the need for surgical incisions, leading to less pain, minimal recovery time, and a lower risk of complications. For men who have undergone a vasectomy, PESA offers an effective alternative to more invasive surgical sperm retrieval methods, allowing them to achieve parenthood with their partner through assisted reproductive technologies.